A native app is an app built for a mobile device and its operating system. A native app is installed directly onto the device. Mobile users will usually acquire these apps through online stores or marketplaces such as The App Store or Google Play.
A mobile web app is an Internet-enabled app that has specific functionality for mobile devices. They’re accessed using the web browser available on the mobile device (for example Safari on the iPhone) and they don’t need to be downloaded or installed on the device.
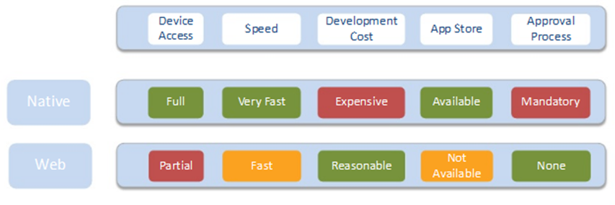
Each have their own strengths and weaknesses as it follows:
Native apps usually perform faster than mobile web apps but mobile web apps have a common code base across all platforms.
App stores and marketplaces help users find native apps but on the other hand, mobile web apps don’t require the users to go to a store, download the app, install the app, update the app and so on.
Native apps make use of all the phone’s features, such as the mobile phone camera, geolocation, and the user’s address book.
Users are asured by the app store approval processes of the quality and safety of the native apps. Mobile web apps can be released much easier in any form and any time because there is no app store that has to approve them.
Native apps are more expensive to develop (especially if we are talking about multiple mobile devices) while mobile web apps can’t access all of the device’s features.
Native app users can and will use different versions of the app, thus making the app harder to maintain and provide support for. On the other hand, the mobile web app users can use different browsers as well, raising the same problem regarding support and maintenance.
Want to build your own native app or a mobile web app? Mobile is not only about choosing between web and native apps. We are here to find the best way that suits your needs.